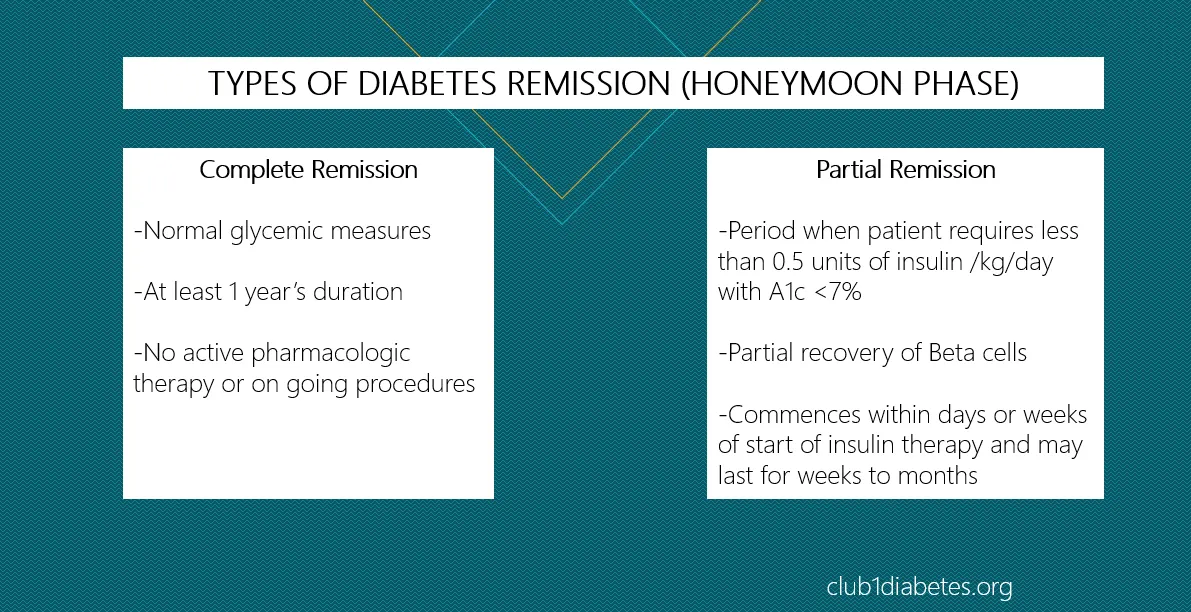
What is the Diabetes Type 1 Honeymoon Phase
The honeymoon phase in type 1 diabetes is a period of remission that often occurs shortly after diagnosis and the initiation of insulin therapy. During this phase, the body still produces some insulin, either naturally or with the help of the insulin injections, leading to a temporary decrease in the required insulin dosage. This period can bring a sense of relief and improved blood sugar control for those recently diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. Understanding this phase is crucial for effective diabetes management, as it impacts insulin needs and the overall approach to care. The duration and intensity of the honeymoon phase vary from person to person, with some experiencing a short period, while others have it for a longer duration.
How Long Does the Honeymoon Phase Last
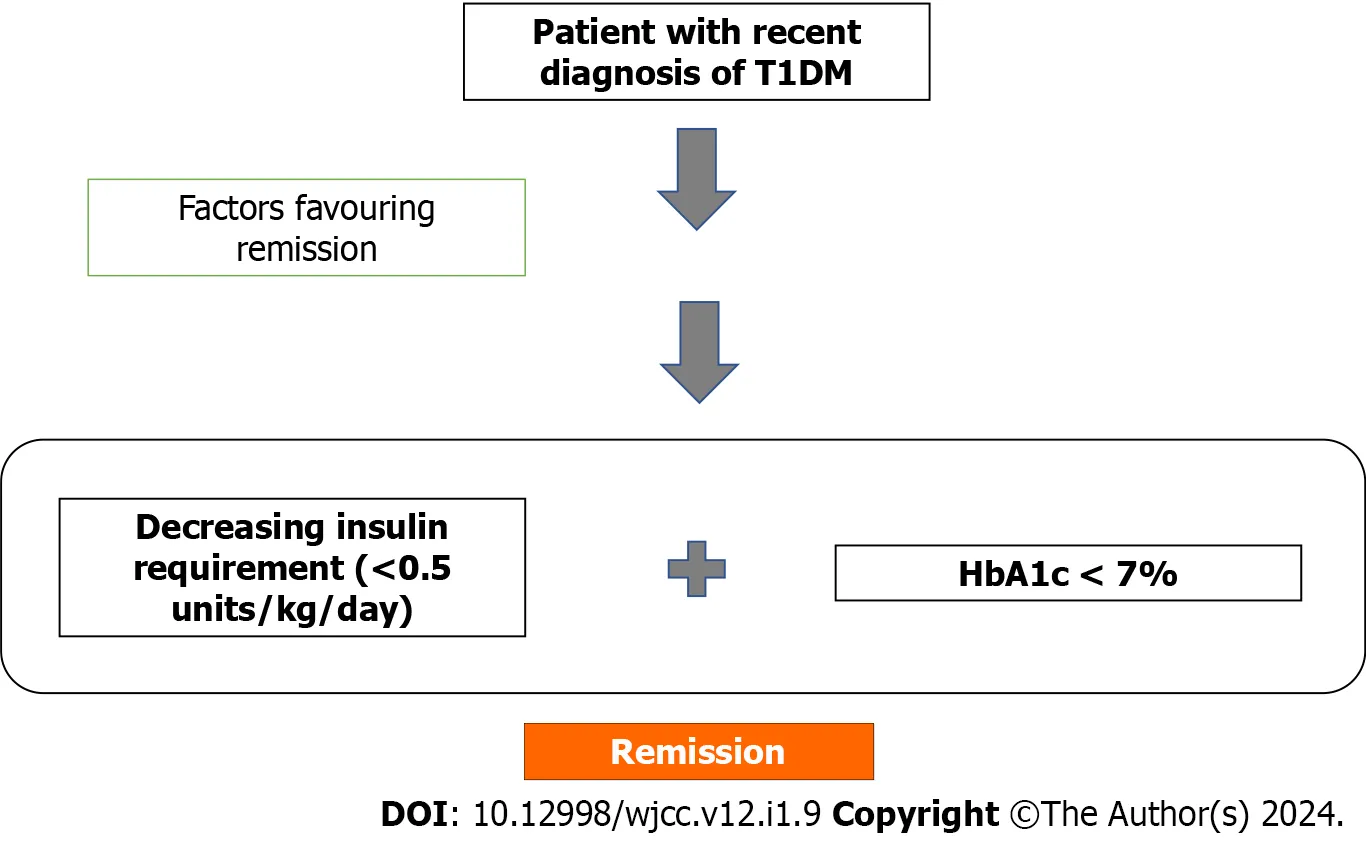
The duration of the honeymoon phase varies significantly. It can last from a few weeks to several months, and in some cases, even up to a year or longer. There’s no definitive answer as to how long it will last because it depends on multiple factors. The end of the honeymoon phase is marked by the gradual decline of the beta-cells. This decline signifies the need for higher insulin dosages as the bodyu2019s insulin production decreases. Regular monitoring and communication with your healthcare team are essential to adapt the insulin therapy as the body’s needs change during this phase.
Factors Influencing Honeymoon Phase Duration
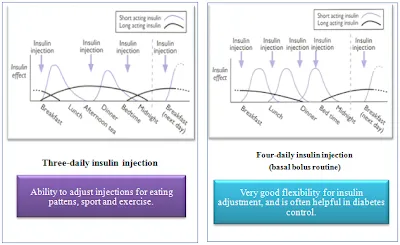
Several factors influence the duration of the honeymoon phase. Early and aggressive insulin therapy, as well as the preservation of some beta-cell function, are key. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and overall health management can play a role. Genetic factors, age at diagnosis, and the severity of the initial diagnosis can all contribute. The extent of residual beta-cell function at the time of diagnosis is also critical. The better the initial metabolic control and adherence to treatment, the longer the honeymoon phase may last. This phase underscores the importance of early, comprehensive diabetes care to maximize the benefits.
Symptoms and Signs of the Honeymoon Phase
Recognizing the symptoms and signs of the honeymoon phase is important for managing diabetes. Itu2019s characterized by a temporary improvement in blood sugar control, sometimes allowing for reduced insulin doses. This period is marked by a decreased need for insulin, fewer instances of high or low blood sugar levels, and a general feeling of improved well-being. This can sometimes be mistaken for a cure, but it’s vital to understand it’s a temporary phase of improved insulin sensitivity. Regular monitoring of blood glucose and a proactive approach to insulin adjustments are required. Education about these changes helps manage expectations and ensure ongoing effective diabetes management.
Improved Blood Sugar Control
During the honeymoon phase, individuals with type 1 diabetes often experience significantly improved blood sugar control. This improvement is due to the body’s residual insulin production, which, combined with insulin therapy, helps maintain blood glucose levels within the target range. The reduced need for insulin injections can make it easier to manage diabetes on a daily basis, decreasing the frequency of highs and lows. Proper blood sugar control during the honeymoon phase can also reduce the risk of both short-term and long-term complications associated with diabetes. Regular monitoring and adapting treatment as needed are very important to maintain the benefits of this period.
Reduced Insulin Needs
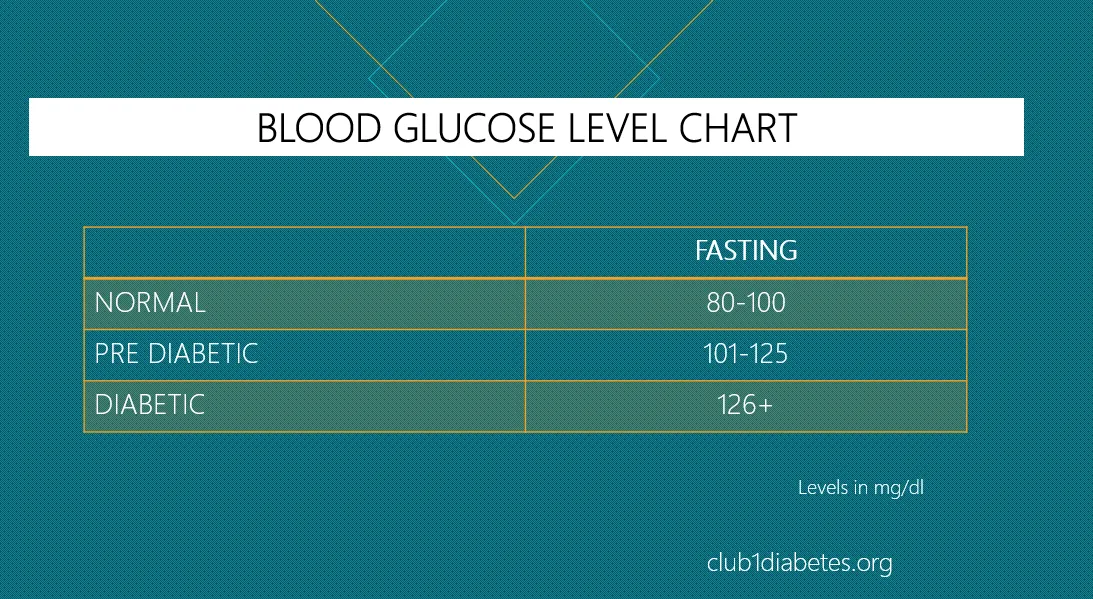
One of the most noticeable signs of the honeymoon phase is a reduced need for insulin. As the body begins to produce more insulin on its own (or with the assistance of injections), the required dosage of injected insulin decreases. This reduction can be a welcome change, lessening the burden of frequent insulin injections and making diabetes management more manageable. It’s essential to monitor blood sugar levels closely during this time and work closely with a healthcare provider to adjust insulin doses accordingly. Ignoring this can lead to hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. Reducing insulin intake is a sign that the body is entering this phase.
Risk of Hypoglycemia
While the honeymoon phase brings positive changes, it also increases the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Because the body’s insulin needs fluctuate, itu2019s essential to carefully monitor blood sugar levels and adjust insulin doses, diet, and exercise routines to prevent blood sugar from dropping too low. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include shakiness, sweating, confusion, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness. Individuals must be vigilant and have a plan to treat low blood sugar quickly, which includes carrying fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets or juice, at all times. Close monitoring and quick action can reduce the risks.
Why the Honeymoon Phase Occurs
The honeymoon phase in type 1 diabetes is a natural process. It’s characterized by a temporary improvement in the body’s ability to manage blood sugar. The exact reasons are multifaceted. It is often associated with a combination of factors, including a partial recovery of beta-cell function and a decreased immune response. Understanding these underlying mechanisms can help in managing expectations and treatment strategies during this phase. It is a dynamic phase where the balance between the body’s insulin production and external insulin administration is constantly changing, so monitoring and proper care are very important.
Immune System Recovery
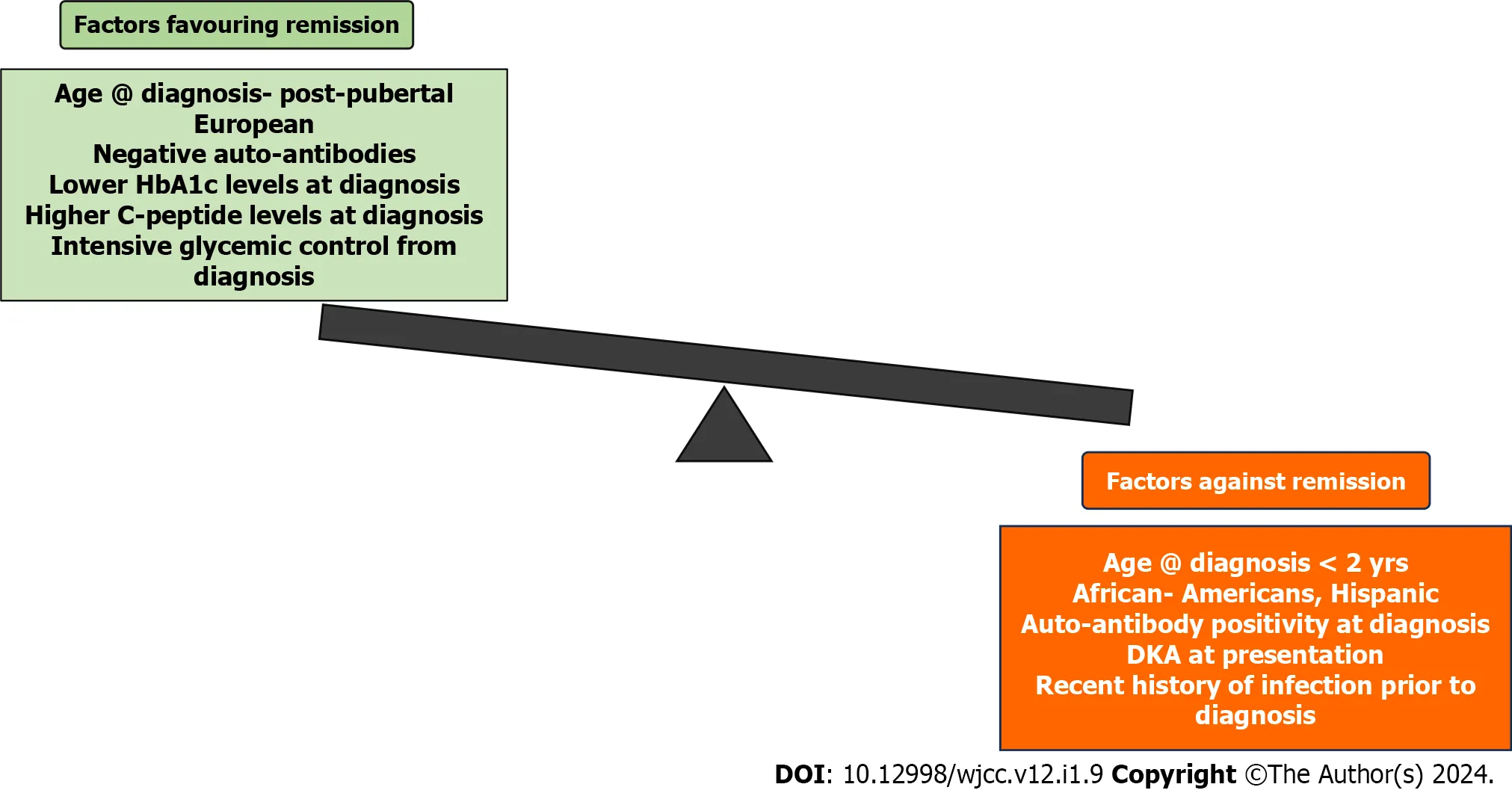
One key aspect of the honeymoon phase is the initial recovery of the immune system. In type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly attacks the beta cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. After the initial diagnosis and start of insulin therapy, the immune response that attacks the beta cells may decrease. This reduced attack allows for some of the remaining beta cells to recover and function more effectively. This recovery may be temporary, but it can lead to improved blood sugar control and a reduced need for external insulin. Immunosuppressant therapies may also influence the honeymoon phase.
Beta-Cell Function
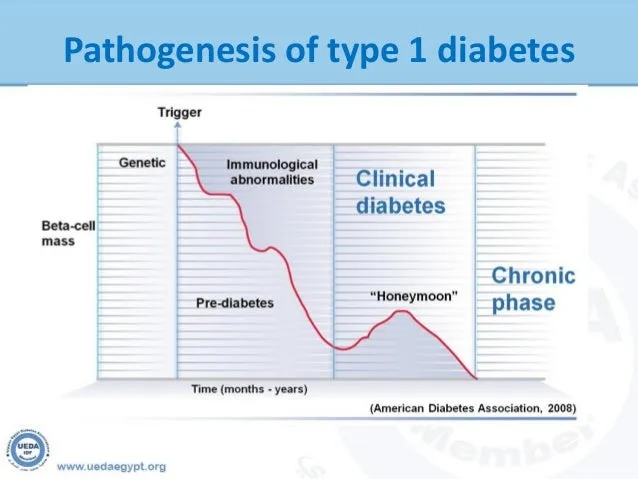
Beta-cell function is another crucial factor in the honeymoon phase. While type 1 diabetes is characterized by the destruction of beta cells, some of these cells may remain functional, especially in the early stages of the disease. With the help of insulin injections, these beta cells might recover some of their function, leading to the production of insulin. The extent of this recovery varies. The improved function of beta cells during the honeymoon phase contributes to better blood sugar control. The amount of time the beta cells function decreases. This is why insulin needs eventually increase.
Managing Diabetes During the Honeymoon Phase
Managing diabetes during the honeymoon phase requires a proactive and adaptable approach. It’s critical to work closely with your healthcare team to regularly monitor blood sugar levels and adjust your insulin dosages accordingly. This includes understanding how lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise impact blood sugar and making necessary adjustments to prevent hypoglycemia. Open communication with your healthcare providers is crucial, as changes in blood sugar control need frequent monitoring. By adopting a flexible and informed approach, individuals can effectively manage their diabetes. They can also maintain their overall health during the honeymoon phase.
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Regular blood glucose monitoring is a cornerstone of diabetes management, especially during the honeymoon phase. Checking blood sugar levels multiple times per day helps to track fluctuations and understand how different factors affect blood glucose. This information enables you to make informed decisions about insulin dosages, diet, and exercise. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) provide real-time glucose readings and can alert users of rapidly changing blood sugar levels. Accurate records allow you to analyze patterns and discuss any adjustments needed with your healthcare provider. The frequency of blood glucose monitoring may vary depending on your individual needs.
Adjusting Insulin Dosage
Adjusting insulin dosages is a key part of managing type 1 diabetes. During the honeymoon phase, insulin needs often decrease, requiring careful monitoring and dose adjustments to avoid hypoglycemia. This is usually done in collaboration with your healthcare team, which may include an endocrinologist, a diabetes educator, or a certified diabetes care and education specialist. You need to frequently review blood sugar readings, carbohydrate intake, and physical activity levels. Insulin doses are adjusted to match changing needs. Being proactive in adjusting dosages is essential for maintaining blood sugar control and preventing complications. Regular check-ins with your healthcare team help ensure that insulin therapy is always appropriate.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle adjustments are critical in managing type 1 diabetes during the honeymoon phase. These include making informed choices about diet and physical activity. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins helps regulate blood sugar levels. Consistent physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, making your body more efficient at using insulin. It’s essential to learn how to calculate carbohydrate intake and match it with appropriate insulin doses to prevent fluctuations. Education and support from a diabetes care team are also key. Regular monitoring of your blood sugar and making adjustments to your lifestyle will improve your overall health.
Diet and Exercise
Diet and exercise play key roles in managing diabetes during the honeymoon phase. A well-balanced diet emphasizes whole foods and limits processed foods and added sugars. Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps regulate blood sugar levels. You should work with a healthcare professional to create a meal plan and exercise routine that are personalized to your needs. It is important to time meals and exercise strategically in conjunction with insulin doses to avoid hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Consistency in diet and exercise is as important as regularly monitoring blood glucose levels, and it forms the foundation of successful diabetes management.
Emotional Support
Receiving emotional support is essential during the honeymoon phase. Adjusting to life with type 1 diabetes can be emotionally challenging. Support from healthcare providers, family, friends, and support groups can provide valuable assistance. Sharing your experiences, concerns, and successes with others who understand can significantly improve your emotional well-being and help you cope with the daily management of diabetes. Consider attending support group meetings or seeking individual counseling to improve your mental health.
Long-Term Outlook and Considerations
Understanding the long-term outlook and considerations is crucial for managing type 1 diabetes. The honeymoon phase is temporary, and eventually, the body’s ability to produce its own insulin will diminish. Effective management involves ongoing adaptation and adjustment of treatment strategies to maintain blood sugar control and prevent complications. This means working closely with your healthcare team to monitor your health and make informed decisions. The long-term health outlook involves adherence to a balanced diet, regular exercise, and the proper management of medications. Continuous learning and support are essential to managing the challenges of type 1 diabetes effectively.
Importance of Continued Care
Maintaining continued care is critical for managing type 1 diabetes effectively, especially after the honeymoon phase ends. Regular check-ups with your endocrinologist, diabetes educator, and other members of your healthcare team are essential. These visits allow for monitoring of blood sugar control, adjustments to insulin dosages, and screening for potential complications. Continuing education about diabetes management is also crucial. Staying informed about the latest advancements in treatment and management strategies empowers you to take charge of your health. Consistent care ensures that you maintain the best possible quality of life despite the ongoing challenges of diabetes.
Potential Complications
Understanding the potential complications is essential for effective long-term diabetes management. Uncontrolled blood sugar can lead to both short-term and long-term health problems. These include hypoglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), and increased risk of heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision loss. Regular check-ups are essential to monitor your health. Early detection and treatment of these complications are vital for preventing serious health problems. Working with your healthcare team to proactively manage your diabetes will minimize the risk and maintain your overall well-being.
The Role of Education and Support
Education and support are the cornerstones of effective diabetes management. Diabetes education empowers individuals to take charge of their health. Learning about blood sugar monitoring, insulin administration, and lifestyle adjustments gives individuals the skills and confidence to manage their condition effectively. Support groups and networks provide a sense of community. These resources can offer valuable insights and encouragement. By seeking out education and support, you equip yourself with the knowledge and tools needed to live a healthy life with type 1 diabetes. Education is very important, and support systems improve the quality of life.
